Jupyter Hub¶
Deprecation Notice
hub.crc.pitt.edu will be retired during the next quarterly maintenance, scheduled for early Jan 2025. Courses should use the new jupyter.crc.pitt.edu that is integrated with the compute nodes on the Teach Cluster. Researchers should use Jupyter through Open On-Demand.
Summary¶
In addition to Jupyter notebook sessions via Open OnDemand, CRCD also hosts the functionality for the multi-user equivalent Jupyter Hub.
Accessing CRCD Jupyter Hub¶
As with any of the other methods for connecting to CRCD resources, you should start by ensuring you have a proper connection to the GlobalProtect VPN. With this connection established, you can proceed with the steps below.
The Server Options dropdown gives you the option to create a Jupyter Hub instance on your local machine, on the SMP cluster (1 core, 3 hours), or on the GPU cluster with GTX 1080 (1 GPU, 3 hours) or A100 (1 GPU, 3 hours).
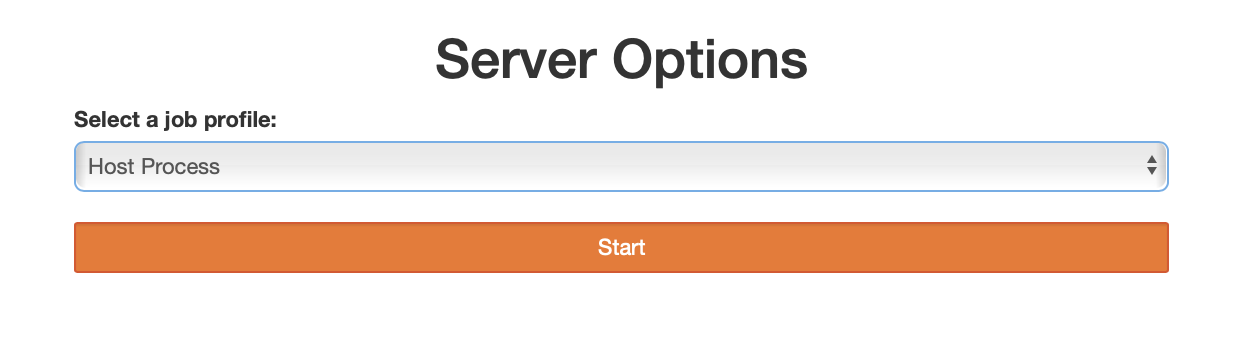
After making your selection, click on Start and you will be redirected once the job is provisioned on the cluster. This may take a few minutes, depending on the cluster's load.
Once the job has started, click on Start My Server, which will lead you to the Launcher page.
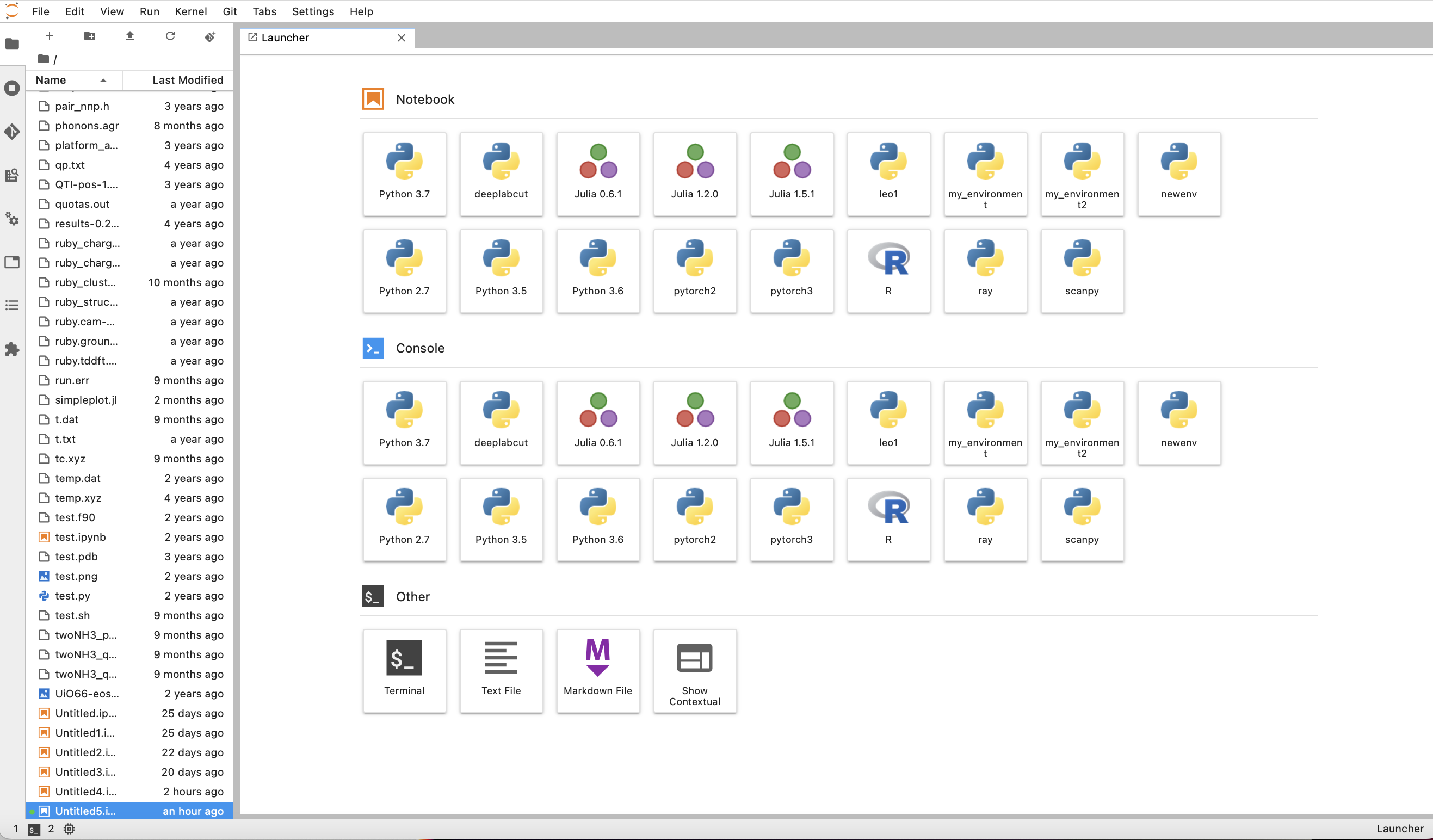
Here you can open a Jupyter notebook, a Console or even a Terminal. Your files stored on the CRCD cluster are visible in the left pane.
Notebooks and Consoles can be started using a specific kernel. Some of these kernels correspond to standard Python (or Julia and R) environments, for instance Python 3.7. Other kernels can contain user-defined virtual environments, with specific packages installed. We provide guidelines on how to create Python virtual environments, install software in them and make them visible as user-defined kernels in Jupyter Hub at python.
General information about Juyter notebook capabilities are available at https://jupyter.org. Jupyter notebooks created using the CRCD Jupyter Hub are automatically saved to your home directory on the CRC cluster. The File menu near the top left corner of Jupyter Hub allows you to rename your files or to save them to non-default directories.